Age-Friendly Healthcare & the 4 M's
According to the US Census Bureau, the US population aged 65+ years is expected to nearly double over the next 30 years, from 43.1 million in 2012 to an estimated 83.7 million in 2050. These demographic advances, however extraordinary, have left our health systems behind as they struggle to reliably provide evidence-based practice to every older adult at every care interaction.
Age-Friendly Health Systems is an initiative of The John A. Hartford Foundation and the Institute for Healthcare Improvement (IHI), in partnership with the American Hospital Association (AHA) and the Catholic Health Association of the United States (CHA), designed to meet this challenge head on.
Age-Friendly Health Systems aim to:
- Follow an essential set of evidence-based practices;
- Cause no harm; and
- Align with What Matters to the older adult and their family caregivers.
What Does It Mean to Be Age-Friendly?
Becoming an Age-Friendly Health System entails reliably providing a set of four evidence-based elements of high-quality care, known as the “4Ms,” to all older adults in your system: What Matters, Medication, Mentation, and Mobility.
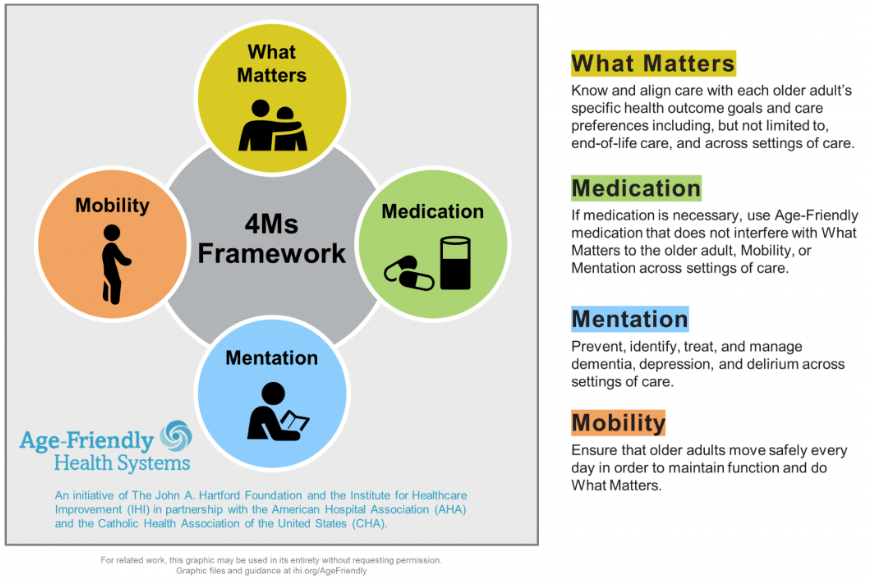
What Matters: What Matters to each older adult, their goals and preferences for care, guides the health care team, and aligns care to what really matters to them.
Medications: Age-related changes can increase the chances of side effects from medications. The health team monitors all medications, decides if medications are still necessary, and ensures older adults’ medications do not interfere with What Matters, Mentation, or Mobility.
Mentation (Mind and Mood): Mental processing, thinking and memory are important! The health team pays attention this this aspect of care, screening for changes that could be related to dementia, depression and delirium.
Mobility: Staying active and moving daily is how older adults stay strong, maintain function, and do What Matters. The health care team ensures safe mobility to keep older adults moving.
What are the levels of recognition for health systems participating in the Age-Friendly Health Systems movement?
IHI recognizes clinical care settings that are working towards reliable practice of evidence-based interventions for all older adults in their care known as the 4Ms (4Ms: What Matters, Medications, Mentation, Mobility). Learn more about the 4Ms in the Age-Friendly Health System Guide to Using the 4Ms in the Care of Older Adults.
Age-Friendly Health System recognitions are made at the facility level including hospitals, practices, nursing homes and convenient care clinics. IHI recognizes care locations at two milestones on their Age-Friendly Health System journey:
-
Level 1: An Age-Friendly Health System Participant has completed a 4Ms Care Description to outline how it will assess, document, and act on all 4Ms at its care setting. At first, their 4Ms Care Description might represent a plan that they will test and work towards reliably performing. 4Ms Care Description fillable PDF forms for submission can be found here.
-
Level 2: An Age-Friendly Health System - Committed to Care Excellence is working towards reliable practice of the 4Ms. They have achieved level 1 and have submitted at least three months of counts of the number of older adults that have received care that included all 4Ms. Counts of older adults reached can be submitted with the bottom portion of the 4Ms Care Description form that was submitted for level 1 recognition.
Age-Friendly Health Care in the New Normal
In 2020 MTGEC's Annual Conference focused on Age-Friendly Healthcare and the 4M's. This conference is now offered online for $35. CLICK HERE for more information and registration.
Age-Friendly Healthcare: micro-presentations
Donald Jurivich, DO: University of North Dakota Department of Geriatrics
Program Director, Dakota Geriatrics Workforce Enhancment Program
